A ridge bone graft is a dental procedure used to augment or build up the height and/or width of the jawbone in preparation for a dental implant. The procedure involves taking bone from another area of the patient’s body or using a synthetic bone graft material to fill in the deficient area of the jawbone.
Before a ridge bone graft, a thorough dental examination will be performed to determine the extent of bone loss and the need for the graft. Dental X-rays or a CT scan may be required to evaluate the condition of the bone and to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
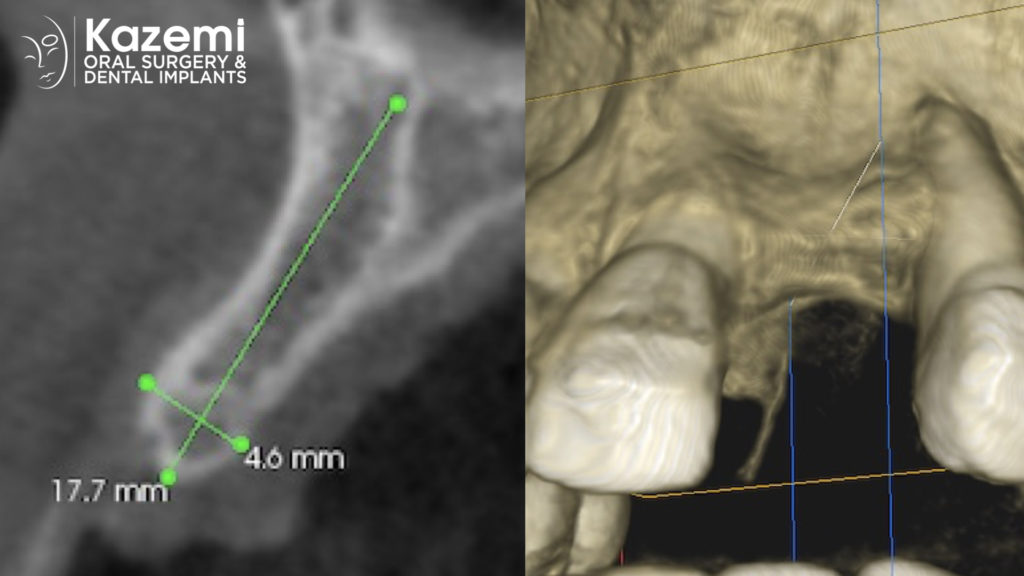
During the ridge bone graft procedure, the patient will receive local anesthesia to numb the treatment area. The graft material is then placed into the deficient area of the jawbone and secured in place with screws or pins. The area is then closed with sutures, and the patient will be given instructions on how to care for the surgical site during the healing process.
After a ridge bone graft, the patient will need to allow time for the bone to heal and integrate with the graft material, a process that can take several months. During this time, the patient may need to follow a soft or liquid diet and avoid putting pressure on the treated area.
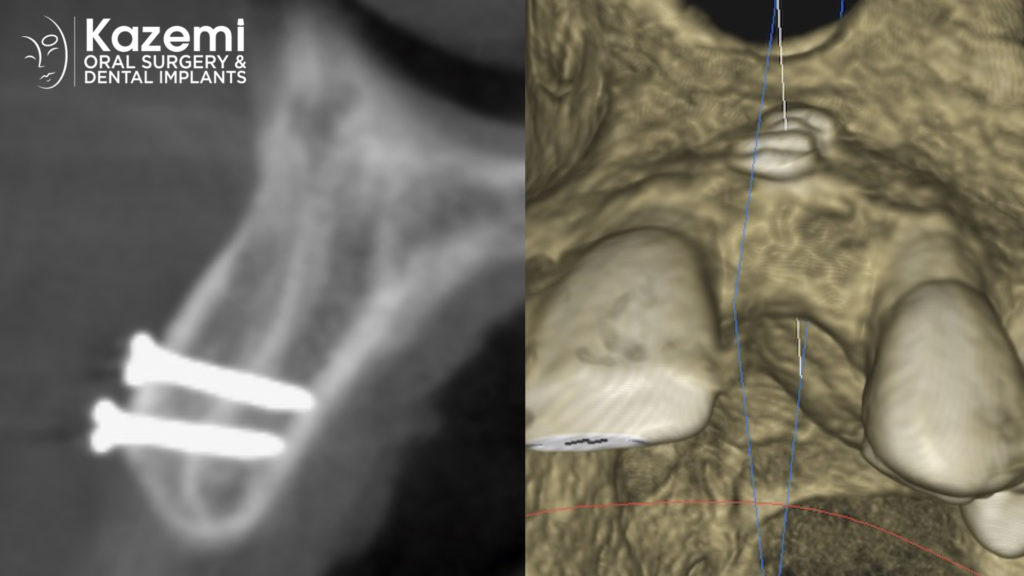
Once the bone has fully healed and integrated with the graft material, the patient may be ready to receive a dental implant. The dental implant will be surgically placed into the jawbone and left to heal for several weeks before a dental crown or other restoration is placed on top of the implant.
Overall, a ridge bone graft can be an effective way to rebuild the jawbone and prepare for dental implant placement. However, the success of the procedure will depend on various factors, such as the quality and quantity of the bone graft material used, the patient’s overall oral health, and their ability to follow post-operative instructions.
Dr. H. Ryan Kazemi is a board-certified oral and maxillofacial surgeon in Bethesda, MD