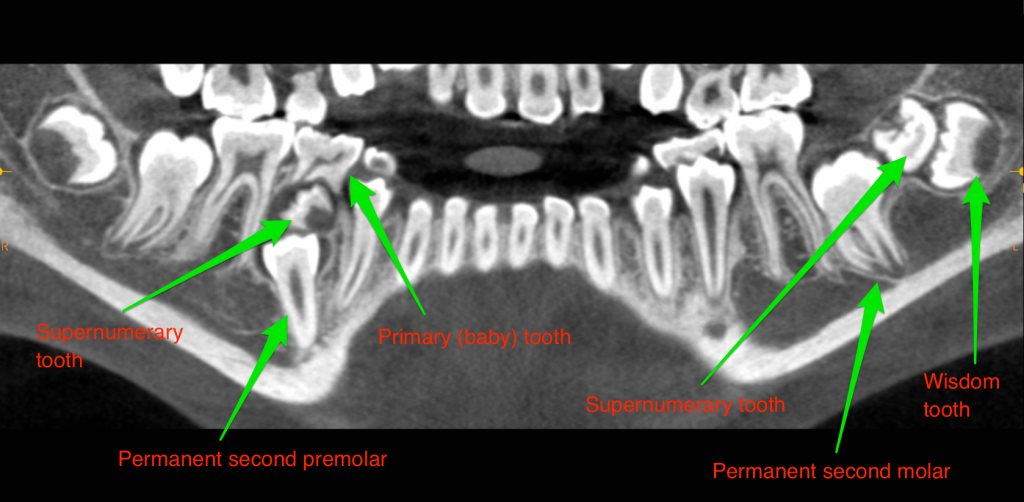
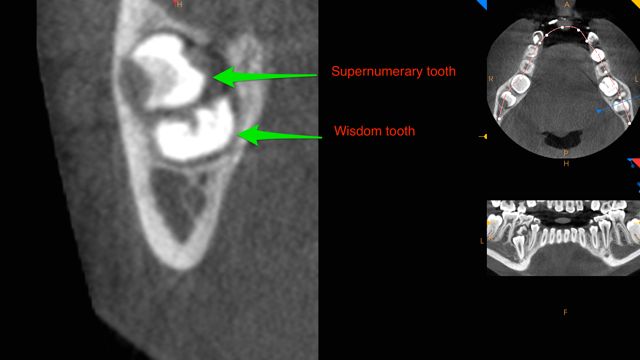
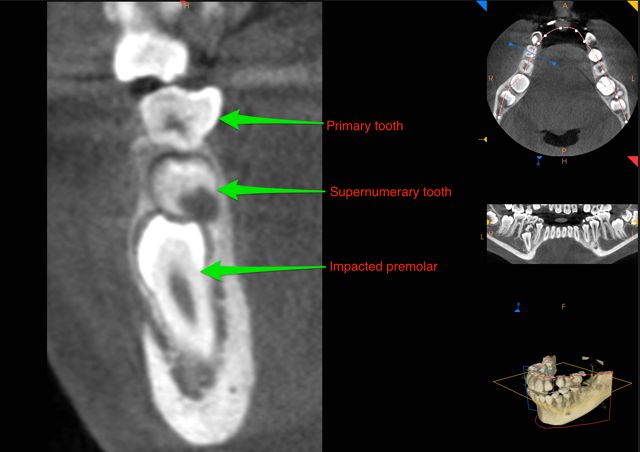
Supernumerary teeth are essentially extra teeth that develop near the erupting permanent teeth. They occur most commonly around wisdom teeth and second premolars. Supernumerary teeth block the permanent teeth from their normal eruption, leading to continued impaction or malposition of the permanent dentition.
Your dentist or orthodontist should closely monitor the eruption of the permanent teeth and any delay should be immediately evaluated and may be recommended for surgical management as appropriate. If not corrected in a timely fashion, the delayed eruption can result in malocclusion (poor bite) and possibly the development of jaw cysts around the impacted permanent teeth.
Here is the timeline for normal eruption of permanent teeth:
- Upper and lower central incisors and lateral incisors should be in the mouth by age 6-7
- Premolars should be in the mouth by age 11-12
- First molars should be in by age 6-7
- Second molars should be in by age 12-13
- Wisdom teeth often remain impacted and do not erupt- but if they do, it occurs at age 18-21
Diagnosis of supernumerary teeth can be made by a conventional panorex or more ideally a CBCT (cone-beam CT scan). Once diagnosed, the dentist or orthodontist should refer the patient to an oral surgeon who will perform the procedure. The approach will consist in the removal of the supernumerary teeth, uncovering of the impacted permanent tooth, extraction of wisdom teeth, and removal of primary teeth as appropriate. Procedures are best performed in the office under IV sedation for optimal comfort.
This 12-year-old patient was seen by his orthodontist who noted a delayed eruption of the right lower premolar and the left lower second molar. Further examination at our office with a CBCT showed supernumerary teeth above the lower left wisdom tooth and the right permanent second premolar. The recommended treatment was to remove both supernumerary teeth, extract the lower left wisdom tooth and the lower right primary (baby) tooth. Following this, the orthodontist will closely monitor the eruption pattern of the permanent left lower second molar and the right lower second premolar. If, by age 13-14 the teeth have not erupted naturally then recommendations may be made for surgical exposure and orthodontic-assisted eruption into the mouth.